101 2 F To C
pachranga
Sep 12, 2025 · 5 min read
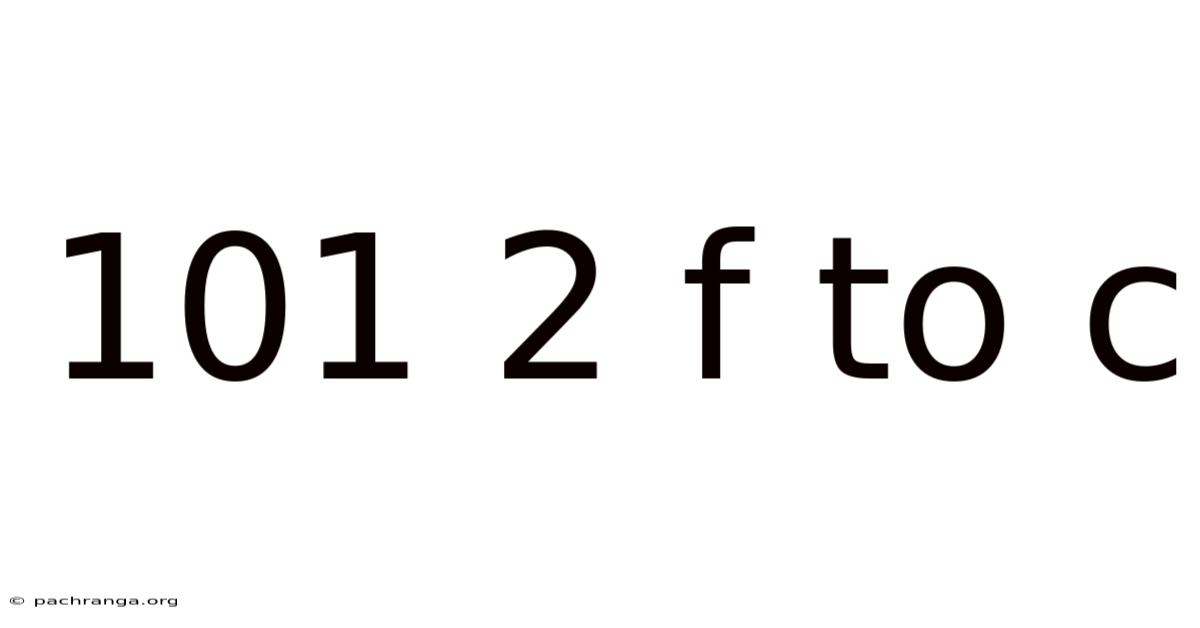
Table of Contents
101 on Converting Fahrenheit to Celsius: A Comprehensive Guide
Converting temperatures between Fahrenheit (°F) and Celsius (°C) might seem like a simple task, but understanding the underlying principles and mastering the conversion process is crucial for various applications, from cooking and everyday life to scientific research and engineering. This comprehensive guide will delve into the "101" of Fahrenheit to Celsius conversion, providing you with not only the formula and practical steps but also a deeper understanding of the scales themselves and their historical context. We'll also explore common misconceptions and address frequently asked questions.
Introduction: Understanding Fahrenheit and Celsius
Before diving into the conversion process, let's briefly understand the two temperature scales. The Fahrenheit scale, developed by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in the early 18th century, is primarily used in the United States. It sets the freezing point of water at 32°F and the boiling point at 212°F, with a difference of 180 degrees between them.
The Celsius scale, also known as the centigrade scale, is a metric unit and is the most widely used temperature scale globally. It defines the freezing point of water as 0°C and the boiling point as 100°C, with a difference of 100 degrees. This consistent 100-degree range between water's freezing and boiling points makes the Celsius scale more intuitive and easier to work with for many scientific and practical purposes.
The Conversion Formula: From Fahrenheit to Celsius
The core of converting Fahrenheit to Celsius lies in a simple yet powerful formula:
°C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
This formula mathematically translates a temperature reading in Fahrenheit to its equivalent in Celsius. Let's break down what each part of the formula represents:
- °F: This represents the temperature value you are starting with, expressed in Fahrenheit.
- - 32: This subtracts the offset between the freezing points of the two scales (32°F).
- × 5/9: This accounts for the different degree sizes between Fahrenheit and Celsius. The ratio 5/9 adjusts the Fahrenheit value to the smaller Celsius degree.
Step-by-Step Guide to Fahrenheit to Celsius Conversion
Let's solidify our understanding with a step-by-step example. Let's convert 77°F to Celsius:
Step 1: Substitute the Fahrenheit value into the formula:
°C = (77 - 32) × 5/9
Step 2: Perform the subtraction:
°C = 45 × 5/9
Step 3: Perform the multiplication:
°C = 25
Therefore, 77°F is equal to 25°C.
Let's try another example: Converting 212°F (boiling point of water) to Celsius.
Step 1: Substitute the Fahrenheit value:
°C = (212 - 32) × 5/9
Step 2: Perform the subtraction:
°C = 180 × 5/9
Step 3: Perform the multiplication:
°C = 100
As expected, the boiling point of water is 100°C.
Practical Applications: Why is Fahrenheit to Celsius Conversion Important?
The ability to convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius is essential in various contexts:
- International Collaboration: In scientific research, engineering, and international collaborations, using a consistent temperature scale (Celsius) is critical for clear communication and data accuracy.
- Cooking and Baking: Many international recipes use Celsius, so understanding the conversion is essential for successful cooking and baking.
- Weather Reports: Understanding global weather patterns often involves comparing temperatures from different regions that may use different scales.
- Medical Applications: Accurate temperature readings are critical in healthcare, and converting between scales is sometimes necessary.
- Understanding Global Climate Data: Analyzing climate change and interpreting global temperature data requires a standardized approach, typically using Celsius.
Beyond the Basics: A Deeper Look at Temperature Scales
The Fahrenheit and Celsius scales are not the only temperature scales in existence. The Kelvin scale is another widely used scale, particularly in scientific applications. The Kelvin scale is an absolute temperature scale, meaning its zero point (0 K) represents absolute zero, the theoretical point at which all molecular motion ceases. This is a significantly lower temperature than the freezing point of water.
The relationship between Kelvin (K) and Celsius (°C) is simple:
K = °C + 273.15
Understanding the relationship between these scales highlights the importance of a standardized temperature measurement system for accurate scientific measurements.
Common Misconceptions and Pitfalls
While the Fahrenheit to Celsius conversion formula is straightforward, some common misconceptions can lead to errors:
- Incorrect Order of Operations: Always remember to follow the order of operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS). Subtraction must be performed before multiplication.
- Mixing Up the Formula: Ensure you use the correct formula. There's a separate formula for converting Celsius to Fahrenheit.
- Using Approximations: While approximations can be useful in everyday situations, accurate conversions require using the full formula.
- Not Accounting for Significant Figures: Pay attention to significant figures in scientific applications to maintain the accuracy of your results.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Why are there two different temperature scales?
A1: Historically, different scales emerged independently. Fahrenheit was developed earlier, while Celsius became more widely adopted due to its inherent simplicity and relationship with the metric system.
Q2: Can I use an online converter instead of the formula?
A2: Online converters are a convenient tool for quick conversions, but understanding the underlying formula is valuable for comprehending the process and for situations where a calculator isn't readily available.
Q3: What is the significance of absolute zero?
A3: Absolute zero (0 K) is the theoretical lowest possible temperature, where all molecular motion ceases. It serves as a fundamental reference point in thermodynamics and other scientific disciplines.
Q4: Is it easier to convert from Celsius to Fahrenheit or vice versa?
A4: The formulas are conceptually similar in their complexity. However, the ratio of 9/5 (for Celsius to Fahrenheit) might seem slightly less intuitive than 5/9 (for Fahrenheit to Celsius) for some individuals.
Q5: Are there any other temperature scales besides Fahrenheit, Celsius, and Kelvin?
A5: Yes, other scales exist, but Fahrenheit, Celsius, and Kelvin are the most commonly used and recognized. These include the Rankine scale and the Réaumur scale.
Conclusion: Mastering Temperature Conversions
Mastering the conversion between Fahrenheit and Celsius is more than just memorizing a formula; it's about understanding the underlying principles of temperature measurement and appreciating the historical context of these scales. This knowledge is valuable across numerous fields, from everyday cooking to advanced scientific research. By understanding the steps involved, avoiding common pitfalls, and appreciating the broader context, you can confidently convert temperatures and communicate effectively in various situations. The simple formula might seem minor, but its applications are far-reaching, contributing to clearer communication and accurate interpretations of data across a wide range of disciplines.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 11c In Fahrenheit
Sep 12, 2025
-
Translate Spanish To English Songs
Sep 12, 2025
-
Gang Hand Signs And Meanings
Sep 12, 2025
-
How Many Pounds Is 220kg
Sep 12, 2025
-
How Long Is 1 5 Centimeters
Sep 12, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 101 2 F To C . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.