101 5 F To C
pachranga
Sep 11, 2025 · 5 min read
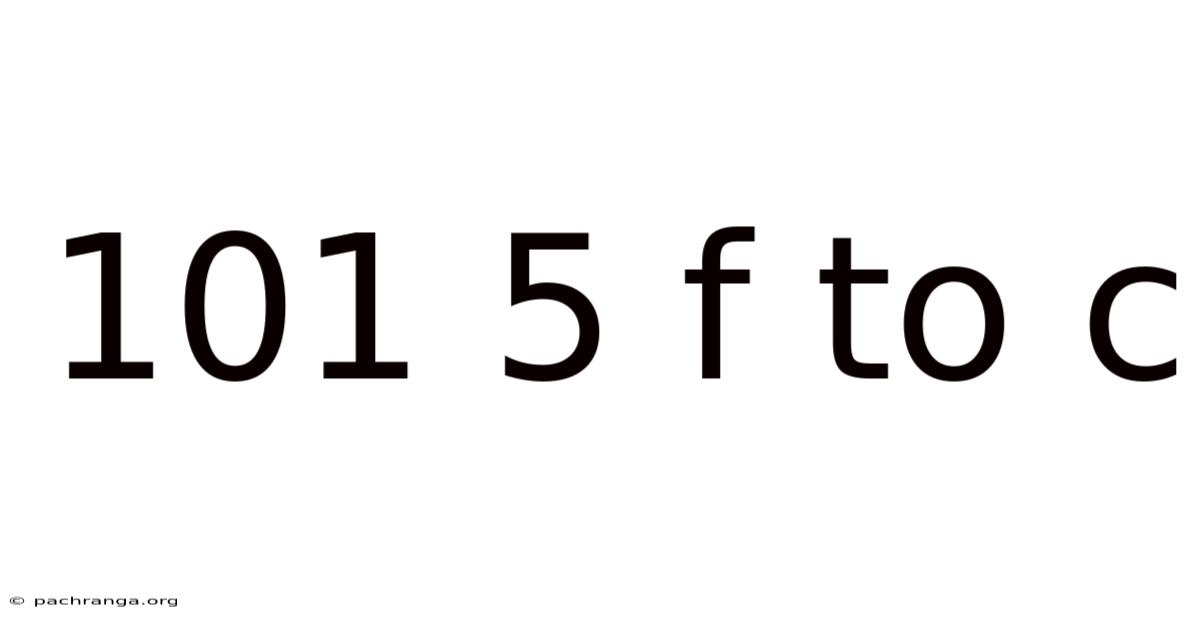
Table of Contents
101 on Converting Fahrenheit to Celsius: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding how to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius is a fundamental skill in many fields, from cooking and baking to meteorology and engineering. While a quick online search might give you the answer, truly grasping the why behind the conversion is crucial for applying this knowledge effectively. This comprehensive guide will not only teach you the how, but also the why, providing a deep dive into the conversion process, its history, and practical applications. We'll even tackle common mistakes and frequently asked questions to ensure you become a Fahrenheit-to-Celsius conversion expert.
Introduction: The Two Major Temperature Scales
The world uses two primary temperature scales: Fahrenheit (°F) and Celsius (°C), also known as Centigrade. Fahrenheit, developed by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in the early 18th century, is predominantly used in the United States, while Celsius, devised by Anders Celsius, is the international standard and preferred scale for scientific applications. The difference lies in the assigned values for the freezing and boiling points of water. Fahrenheit sets the freezing point of water at 32°F and the boiling point at 212°F, while Celsius assigns 0°C to freezing and 100°C to boiling. This difference in base points necessitates a conversion formula to move between these scales.
Understanding the Conversion Formula: The Math Behind the Magic
The formula for converting Fahrenheit (°F) to Celsius (°C) is:
°C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
Let's break this down step-by-step:
-
Subtract 32: The first step involves subtracting 32 from the Fahrenheit temperature. This is because the zero point of the Fahrenheit scale is 32 degrees below the freezing point of water on the Celsius scale. This adjustment aligns the two scales' reference points.
-
Multiply by 5/9: The second step involves multiplying the result by 5/9. This accounts for the different degree sizes between the two scales. A change of 1°C is equivalent to a change of 1.8°F (9/5°F). Multiplying by 5/9 effectively scales down the Fahrenheit value to the equivalent Celsius value.
Example: Let's convert 68°F to Celsius.
- 68°F - 32°F = 36°F
- 36°F × 5/9 = 20°C
Therefore, 68°F is equal to 20°C.
Practical Applications: When is Fahrenheit to Celsius Conversion Essential?
The ability to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius is vital in various aspects of daily life and professional work. Here are some key examples:
-
Cooking and Baking: Many international recipes use Celsius, while American recipes often use Fahrenheit. Accurate conversion is crucial for achieving desired results. Incorrect temperature can result in undercooked or overcooked food.
-
Medical Field: Body temperature, often measured in Fahrenheit in some regions, needs to be converted to Celsius for accurate medical records and diagnosis. International medical standards use Celsius.
-
Meteorology and Climate Science: Global weather reports and climate data are largely presented in Celsius. Understanding these reports requires conversion skills, especially for those in regions primarily using Fahrenheit.
-
Engineering and Manufacturing: Many engineering and manufacturing processes require precise temperature control. Converting between Fahrenheit and Celsius ensures accuracy and consistency in these applications.
-
Science Experiments: Scientific research often relies on precise temperature measurements and calculations. The international scientific community predominantly uses the Celsius scale.
Common Mistakes to Avoid: Pitfalls in Conversion
While the formula is relatively straightforward, several common mistakes can lead to inaccurate conversions. Avoid these pitfalls:
-
Incorrect Order of Operations: Always subtract 32 before multiplying by 5/9. Reversing the order will produce an incorrect result.
-
Fractional Errors: Ensure accurate multiplication and division when working with the fraction 5/9. Using a calculator can help avoid errors.
-
Unit Confusion: Always double-check your units. Make sure you're working with Fahrenheit and converting to Celsius, not the other way around.
-
Rounding Errors: While rounding is sometimes necessary, avoid excessive rounding, as it can accumulate error, especially in scientific contexts.
Beyond the Basics: Celsius to Fahrenheit Conversion and the Absolute Scale
While this guide focuses on Fahrenheit to Celsius conversion, understanding the reverse process is equally important. The formula for converting Celsius (°C) to Fahrenheit (°F) is:
°F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
Note that this is simply a rearrangement of the original formula.
Furthermore, it's beneficial to understand the concept of the absolute temperature scale, specifically Kelvin (K). Kelvin is a thermodynamic temperature scale where 0 K represents absolute zero, the theoretical point where all molecular motion ceases. The relationship between Celsius and Kelvin is:
K = °C + 273.15
Understanding these relationships provides a more holistic understanding of temperature scales and their interconnections.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Can I use an online converter instead of doing the calculation manually?
A: Yes, online converters are readily available and can provide quick and accurate conversions. However, understanding the underlying formula is essential for applying the knowledge in various situations and for troubleshooting potential errors.
Q: What if I need to convert a temperature range rather than a single temperature point?
A: Convert each endpoint of the range separately using the formula. This will give you the equivalent range in Celsius.
Q: Are there any alternative methods for Fahrenheit to Celsius conversion?
A: While the formula is the most accurate and widely accepted method, some approximate conversion methods exist. However, these methods are less precise and should be avoided in scenarios requiring accuracy.
Q: Why is Celsius preferred in science and internationally?
A: The Celsius scale is based on the easily reproducible freezing and boiling points of water, making it a more consistent and internationally recognized standard for scientific measurements and data reporting.
Conclusion: Mastering Fahrenheit to Celsius Conversion
Mastering the conversion between Fahrenheit and Celsius is a valuable skill that extends beyond simple calculations. It's about understanding the fundamental principles behind different temperature scales, appreciating the historical context, and recognizing its diverse applications. By avoiding common mistakes and understanding the broader context of temperature measurement, you can confidently navigate the world of temperature conversions and apply this knowledge effectively in various contexts. Remember the formula, practice consistently, and you'll be a Fahrenheit-to-Celsius conversion pro in no time!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
88 Km H To Mph
Sep 11, 2025
-
Convert 68 Celsius To Fahrenheit
Sep 11, 2025
-
900 Degrees Celsius To Fahrenheit
Sep 11, 2025
-
5 Degrees Centigrade In Fahrenheit
Sep 11, 2025
-
66 Cm Converted To Inches
Sep 11, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 101 5 F To C . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.