101 7 F To C
pachranga
Sep 15, 2025 · 5 min read
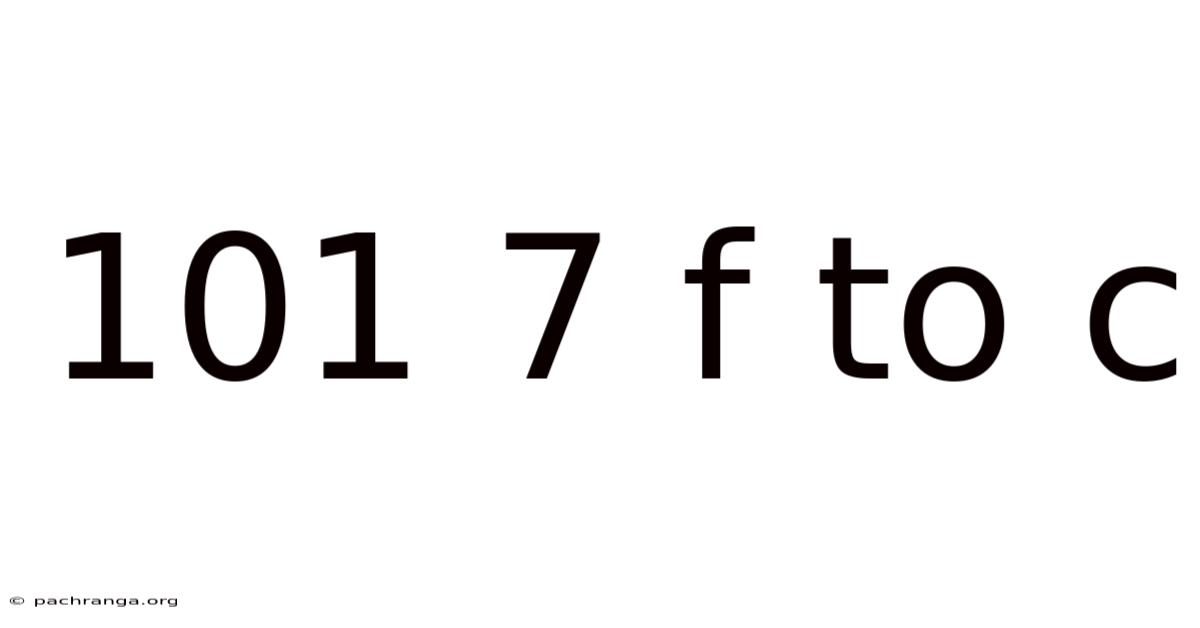
Table of Contents
101 on Converting Fahrenheit to Celsius: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding temperature conversions is crucial in many fields, from cooking and everyday life to science and engineering. This comprehensive guide delves into the art and science of converting Fahrenheit (°F) to Celsius (°C), providing you with not just the formula but also a deep understanding of its application and the underlying principles. We'll cover everything from the basic conversion method to troubleshooting common mistakes and exploring the historical context of these temperature scales. By the end, you'll be a Fahrenheit-to-Celsius conversion expert!
Introduction: Fahrenheit vs. Celsius
The world uses two primary temperature scales: Fahrenheit (°F) and Celsius (°C). While Celsius is the standard in most of the world and the preferred system in scientific contexts, Fahrenheit remains common in the United States. Knowing how to convert between these scales is essential for clear communication and accurate calculations across various applications. This guide will provide you with the tools and knowledge to seamlessly switch between these two systems.
The Fundamental Formula: Converting Fahrenheit to Celsius
The core of the conversion lies in a simple yet powerful formula:
°C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
Let's break this down:
- °F: This represents the temperature in Fahrenheit that you want to convert.
- - 32: We subtract 32 because 0°C is equivalent to 32°F. This accounts for the difference in the freezing point of water between the two scales.
- × 5/9: This is the scaling factor. A degree Celsius is larger than a degree Fahrenheit; 5/9 represents this ratio of magnitude.
This formula allows for precise conversion of any Fahrenheit temperature to its Celsius equivalent.
Step-by-Step Guide to Fahrenheit to Celsius Conversion
Let's solidify this understanding with a step-by-step example: Let's convert 68°F to Celsius.
Step 1: Substitute the Fahrenheit value into the formula.
°C = (68 - 32) × 5/9
Step 2: Perform the subtraction within the parentheses.
°C = (36) × 5/9
Step 3: Perform the multiplication.
°C = 20
Therefore, 68°F is equivalent to 20°C.
Practical Applications: Beyond the Formula
The formula is straightforward, but its applications are vast. Here are some real-world examples:
- Cooking: Recipes often include temperatures in either Fahrenheit or Celsius. Knowing how to convert ensures you achieve the desired cooking results. For instance, if a recipe calls for 350°F, you can easily convert it to Celsius for ovens using the Celsius scale.
- Weather: Understanding temperature conversions allows you to easily interpret weather reports from different regions. A news report from the US might give a temperature in Fahrenheit while another from Europe gives it in Celsius.
- Science and Engineering: Scientific experiments and engineering designs frequently require accurate temperature readings and calculations. Converting between Fahrenheit and Celsius is crucial for maintaining consistent and accurate data.
- Medicine: Body temperature is often measured in either Fahrenheit or Celsius depending on the region and equipment used. Conversion is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Understanding the Historical Context: Why Two Scales?
The existence of two major temperature scales, Fahrenheit and Celsius, reflects the historical development of thermometry. Gabriel Daniel Fahrenheit developed his scale in the early 18th century, basing it on a mixture of ice, water, and ammonium chloride, and human body temperature. Anders Celsius, in the mid-18th century, created his scale with the freezing and boiling points of water as its reference points, leading to the centigrade scale (later renamed Celsius). These differences in development resulted in the different scales we use today.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Concepts and Considerations
While the basic formula is sufficient for most conversions, let's delve into some more advanced considerations:
- Negative Temperatures: The formula works equally well for negative Fahrenheit temperatures. For example, converting -4°F would involve substituting -4 for °F in the formula. Remember to follow the order of operations.
- Precision and Rounding: Depending on the context, you may need to round your answer to a certain number of decimal places. For general purposes, one or two decimal places are usually sufficient, while scientific applications may require greater precision.
- Alternative Methods: While the formula is the most accurate method, you can also use online converters or specialized calculators for quick conversions, especially when dealing with multiple conversions or complex calculations.
Troubleshooting Common Mistakes
Even a simple formula can trip up beginners. Here are common errors and how to avoid them:
- Order of Operations: Always remember to perform the subtraction before the multiplication.
- Incorrect Fraction: Ensure you use 5/9 correctly – it's not 9/5.
- Unit Confusion: Double-check that you are working with Fahrenheit and not another scale like Kelvin.
- Calculator Errors: Make sure you enter the numbers correctly into your calculator and that you are using the correct order of operations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Is there a formula to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit?
A: Yes, the reverse conversion uses the formula: °F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
Q: Why is there a -32 in the Fahrenheit to Celsius conversion?
A: The -32 accounts for the difference in the freezing point of water between the two scales (0°C = 32°F).
Q: Can I use this formula for extremely high or low temperatures?
A: While the formula is generally applicable, for extremely high or low temperatures, you might encounter limitations due to the physical properties of the materials being measured.
Q: What is the difference between Celsius and Centigrade?
A: Historically, Celsius was known as Centigrade. However, the term "Celsius" is now the officially accepted term.
Q: Are there any other temperature scales besides Fahrenheit and Celsius?
A: Yes, the Kelvin scale is another important temperature scale, widely used in science and engineering. It's an absolute temperature scale, meaning 0 Kelvin represents absolute zero.
Conclusion: Mastering Fahrenheit to Celsius Conversion
Mastering Fahrenheit to Celsius conversion empowers you with a practical skill applicable in various aspects of daily life and professional pursuits. From cooking and weather forecasting to scientific research and engineering, understanding this conversion is essential for accurate communication and reliable calculations. By understanding the formula, its applications, and common pitfalls, you can confidently navigate the world of temperature conversions and appreciate the historical context that shaped our understanding of heat and temperature. Remember to practice regularly to solidify your understanding and become a proficient converter. With practice, this seemingly simple conversion becomes second nature, enabling you to effortlessly move between Fahrenheit and Celsius with accuracy and confidence.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Celebrity With A Disability
Sep 15, 2025
-
What Is 45f In Celsius
Sep 15, 2025
-
160 Kg Converted To Pounds
Sep 15, 2025
-
70 Degrees Farenheit In Celcius
Sep 15, 2025
-
How Tall Is 189 Cm
Sep 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 101 7 F To C . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.