130 Deg F To C
pachranga
Sep 10, 2025 · 5 min read
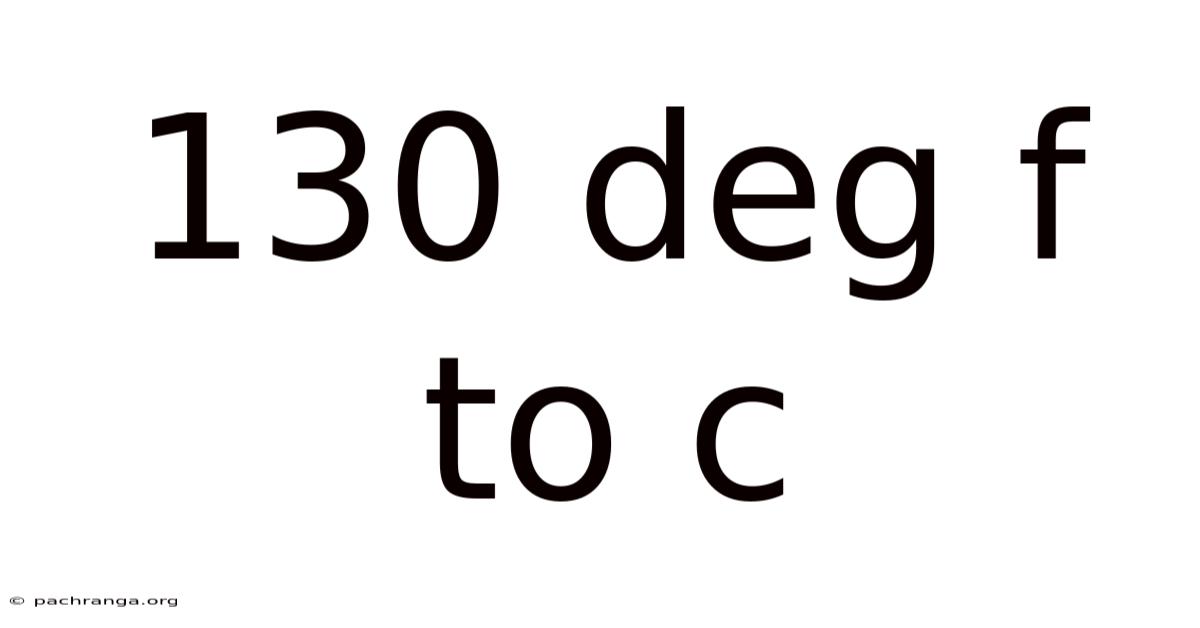
Table of Contents
130°F to °C: Understanding Temperature Conversions and Their Applications
Converting temperatures between Fahrenheit (°F) and Celsius (°C) is a fundamental skill in many fields, from cooking and baking to science and engineering. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the conversion of 130°F to °C, explain the underlying formulas, and explore the practical applications of this conversion in various contexts. We'll also delve into the history of these temperature scales and answer some frequently asked questions. Understanding temperature conversion not only helps in everyday tasks but also lays a crucial foundation for scientific understanding and problem-solving.
Understanding Fahrenheit and Celsius Scales
Before diving into the conversion, let's briefly review the Fahrenheit and Celsius scales. Both are temperature scales used to measure heat and cold, but they differ in their reference points.
-
Fahrenheit (°F): This scale was developed by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in the early 18th century. It sets the freezing point of water at 32°F and the boiling point at 212°F, with a difference of 180 degrees between them.
-
Celsius (°C): Also known as the centigrade scale, this system was developed by Anders Celsius in the mid-18th century. It defines the freezing point of water as 0°C and the boiling point as 100°C, with a difference of 100 degrees.
The difference in reference points and scale intervals makes direct comparison between Fahrenheit and Celsius readings impossible without conversion.
Converting 130°F to Celsius (°C)
The formula to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius is:
°C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
Let's apply this formula to convert 130°F:
°C = (130 - 32) × 5/9 = 98 × 5/9 = 54.44°C (approximately)
Therefore, 130°F is equal to approximately 54.44°C.
Step-by-Step Conversion Process
To ensure clarity, let's break down the conversion process step-by-step:
-
Subtract 32: Start by subtracting 32 from the Fahrenheit temperature (130°F - 32°F = 98°F). This step adjusts for the difference in the freezing point of water between the two scales.
-
Multiply by 5/9: Next, multiply the result from step 1 by 5/9 (98°F × 5/9 ≈ 54.44°C). This accounts for the difference in the scale intervals between Fahrenheit and Celsius.
-
Result: The final result is the equivalent temperature in Celsius.
Practical Applications of 130°F (54.44°C)
A temperature of 130°F (54.44°C) falls within a range relevant to several applications:
-
Cooking and Baking: This temperature is often used in various cooking and baking processes. For example, it might be used for simmering sauces, candy making, or maintaining a specific temperature in an oven for certain types of baking.
-
Industrial Processes: Many industrial processes, especially those involving heating or cooling, operate at or near this temperature range. Examples include certain chemical reactions, material processing, and heat treatment.
-
Medical Applications: While not directly a body temperature, this temperature range might be relevant in certain medical applications, such as sterilizing equipment or maintaining specific incubation conditions.
-
Environmental Monitoring: In some environments, a temperature of 54.44°C could signify a certain level of heat stress or be relevant to studying climate patterns or ecological processes.
The Importance of Accurate Temperature Conversion
Accurate temperature conversion is crucial for a variety of reasons:
-
Safety: In many industrial and scientific applications, precise temperature control is essential for safety. Incorrect conversions can lead to equipment malfunction, hazardous conditions, or inaccurate experimental results.
-
Efficiency: In manufacturing and other processes, accurate temperature control is critical for efficiency and achieving desired outcomes. Improper temperature adjustments can lead to wasted materials, energy, and time.
-
Reproducibility: In scientific research, accurate temperature conversion is necessary to ensure that experiments are reproducible and results are reliable.
-
Global Communication: With the increasingly globalized nature of science, engineering, and many other fields, standardized temperature scales are crucial for clear communication and collaboration.
Further Exploration: Other Temperature Scales
While Fahrenheit and Celsius are the most commonly used scales, others exist, including:
-
Kelvin (K): This absolute temperature scale is widely used in scientific applications. It sets absolute zero (0 K) as the theoretical point where all molecular motion ceases. The conversion from Celsius to Kelvin is straightforward: K = °C + 273.15.
-
Rankine (°R): This absolute temperature scale is based on the Fahrenheit scale. The conversion from Fahrenheit to Rankine is: °R = °F + 459.67.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Why are there two different temperature scales?
A: Historically, different scales developed independently, and each scale reflects different practical needs and reference points at the time of their invention. While Celsius is preferred for scientific applications due to its decimal-based system, Fahrenheit remains in use in certain regions and industries.
Q: Can I use an online converter instead of the formula?
A: Yes, many online converters are available for Fahrenheit to Celsius conversion. However, understanding the formula is crucial for a deeper understanding of the underlying principles and for situations where an online converter isn't available.
Q: What are some common errors in temperature conversions?
A: Common errors include incorrect order of operations (subtracting 32 before multiplying by 5/9), incorrect use of the conversion factor (5/9 or 9/5), and forgetting to add or subtract 32 when converting between absolute and relative scales.
Q: Are there any situations where the approximation of 54.44°C is not sufficient?
A: In scientific and industrial applications where high precision is required, using the full decimal value or employing higher precision in calculations might be necessary. The level of precision required depends on the specific application and tolerance limits.
Conclusion
Converting 130°F to Celsius highlights the importance of understanding temperature scales and their conversion methods. The seemingly simple conversion of 130°F to approximately 54.44°C reveals a deeper connection between different measurement systems and underscores the significance of accurate conversions in various fields. This knowledge empowers us to tackle problems involving temperature effectively and fosters a deeper understanding of the physical world around us. By mastering this fundamental concept, individuals can confidently tackle various applications ranging from everyday cooking to complex scientific endeavors, ensuring safety, efficiency, and accuracy in their work.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 140lb In Kg
Sep 10, 2025
-
How Tall Is 171 Cm
Sep 10, 2025
-
140 Grados Centigrados A Fahrenheit
Sep 10, 2025
-
Whats 200 Pounds In Kg
Sep 10, 2025
-
16 Degrees Celsius To F
Sep 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 130 Deg F To C . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.