15 Deg C Deg F
pachranga
Sep 14, 2025 · 5 min read
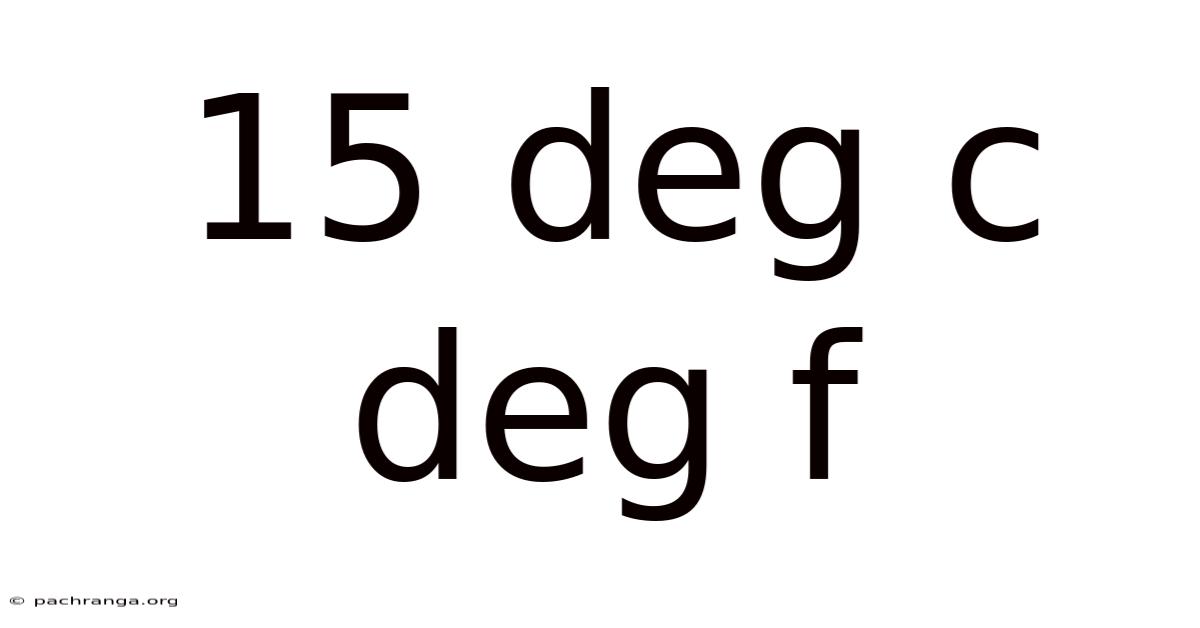
Table of Contents
15°C: Understanding Celsius, Fahrenheit, and the Significance of This Temperature
The seemingly simple question, "What is 15°C in Fahrenheit?" opens a window into the fascinating world of temperature scales and their practical applications. This article will not only answer that question but will delve deeper into the significance of 15°C, exploring its context in various fields, its implications for human comfort, and the science behind the conversion process. We'll also tackle common misconceptions and frequently asked questions surrounding Celsius and Fahrenheit. Understanding temperature conversions is crucial in numerous fields, from meteorology and cooking to engineering and medicine.
Understanding Temperature Scales: Celsius and Fahrenheit
Before we dive into the conversion, let's establish a foundational understanding of the two most common temperature scales: Celsius (°C) and Fahrenheit (°F).
-
Celsius (°C): Also known as the centigrade scale, Celsius is a metric unit based on the freezing and boiling points of water. Water freezes at 0°C and boils at 100°C at standard atmospheric pressure. This scale is widely used globally, particularly in scientific contexts and most countries worldwide.
-
Fahrenheit (°F): The Fahrenheit scale is primarily used in the United States and a few other countries. Its origins are less straightforward, based on a mixture of brine and ice. Water freezes at 32°F and boils at 212°F at standard atmospheric pressure.
Converting 15°C to Fahrenheit
The conversion from Celsius to Fahrenheit is a straightforward mathematical calculation. The formula is:
°F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
Applying this formula to 15°C:
°F = (15 × 9/5) + 32 = 27 + 32 = 59°F
Therefore, 15°C is equal to 59°F.
The Significance of 15°C (59°F)
15°C represents a pleasant and relatively mild temperature for many people. Its significance varies depending on the context:
-
Human Comfort: Many would consider 15°C to be a comfortable temperature, especially indoors. It's often described as cool rather than cold, generally avoiding the discomfort associated with extreme temperatures. However, personal preference plays a significant role; some might find it chilly, while others may perceive it as warm depending on individual tolerances and acclimatization.
-
Climate and Weather: A temperature of 15°C is indicative of a moderate climate. It's often found in spring or autumn in temperate regions, representing a transitional period between warmer and colder seasons. In certain parts of the world, 15°C might represent a typical daytime temperature year-round.
-
Agriculture and Horticulture: 15°C is a vital temperature for many plants. Many crops thrive within a specific temperature range, and 15°C might fall within the optimal growing conditions for certain species. It's also relevant in horticulture, influencing the growth rates and flowering times of various plants.
-
Industry and Engineering: In various industrial processes, maintaining a specific temperature is critical. 15°C might represent a target temperature in certain manufacturing processes or storage conditions for sensitive materials. Precision temperature control is essential for ensuring product quality and safety.
-
Aquatic Environments: 15°C is a common temperature in certain aquatic environments, particularly in temperate lakes and rivers. This temperature significantly affects the behavior and survival of aquatic organisms. The distribution and abundance of fish and other aquatic life can be directly influenced by water temperature.
Beyond the Conversion: Understanding the Underlying Physics
The conversion formula itself masks the underlying physical principles. The difference between Celsius and Fahrenheit stems from the different choices for the fixed points (freezing and boiling points of water) and the scale's interval divisions. The formula’s 9/5 ratio reflects the different size of the degrees between the two scales: a 9°F change corresponds to a 5°C change. The +32 adjusts for the different zero points.
Understanding these underlying physical principles helps us appreciate the significance of temperature scales beyond mere numerical conversions. It connects the seemingly simple mathematical formula to the fundamental properties of matter and energy.
Common Misconceptions about Celsius and Fahrenheit
-
The "Feels Like" Temperature: Often, weather reports provide a "feels like" temperature, which takes into account factors like wind chill and humidity. This is not a direct conversion between Celsius and Fahrenheit but a measure of the perceived temperature based on the combined effects of temperature and other atmospheric conditions. It's important to differentiate between the actual air temperature (measured in °C or °F) and the perceived temperature.
-
Absolute Zero: Both Celsius and Fahrenheit are relative scales; they don't represent the true absence of heat. The absolute zero point, the theoretical lowest temperature possible, is represented differently in each scale. In Kelvin (another important temperature scale), absolute zero is 0K, which is equivalent to -273.15°C or -459.67°F.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: Why are there two different temperature scales?
A: Historically, different scales developed independently. Fahrenheit emerged earlier, while Celsius, with its more logical structure based on the properties of water, gained widespread acceptance, especially in scientific communities. The continued use of Fahrenheit, particularly in the United States, is largely due to inertia and cultural factors.
-
Q: Which scale is better?
A: There's no inherently "better" scale. Celsius is favoured globally due to its simplicity and logical structure, based on the readily observable freezing and boiling points of water. Fahrenheit's continued use reflects historical precedent and cultural factors. The choice often depends on the context and regional conventions.
-
Q: How can I convert Fahrenheit to Celsius?
A: The reverse conversion formula is: °C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
-
Q: Are there other temperature scales?
A: Yes, the Kelvin scale is an absolute temperature scale, widely used in scientific applications. It starts at absolute zero (0 K), where all molecular motion ceases. Other historical scales exist, but they are less commonly used today.
Conclusion: The Broader Implications of Understanding 15°C
Understanding temperature scales, including the conversion between Celsius and Fahrenheit, is far more than just a mathematical exercise. It provides a window into various scientific, practical, and everyday aspects of our lives. From understanding weather patterns and ensuring optimal agricultural practices to controlling industrial processes and maintaining comfortable living conditions, grasping the meaning and implications of a seemingly simple temperature like 15°C is vital. This knowledge empowers us to better understand and interact with the world around us. While the conversion itself is straightforward, the underlying concepts and practical implications are rich and far-reaching. Hopefully, this article has clarified the significance of 15°C and provided a deeper appreciation for the science and practical application of temperature scales.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
1 58 Cm In Feet
Sep 14, 2025
-
One Hundredth Of A Meter
Sep 14, 2025
-
175 Cm To Feet Inches
Sep 14, 2025
-
Convert 55 Fahrenheit To Celsius
Sep 14, 2025
-
300 C Is What Fahrenheit
Sep 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 15 Deg C Deg F . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.