26 Degrees C In F
pachranga
Sep 18, 2025 · 5 min read
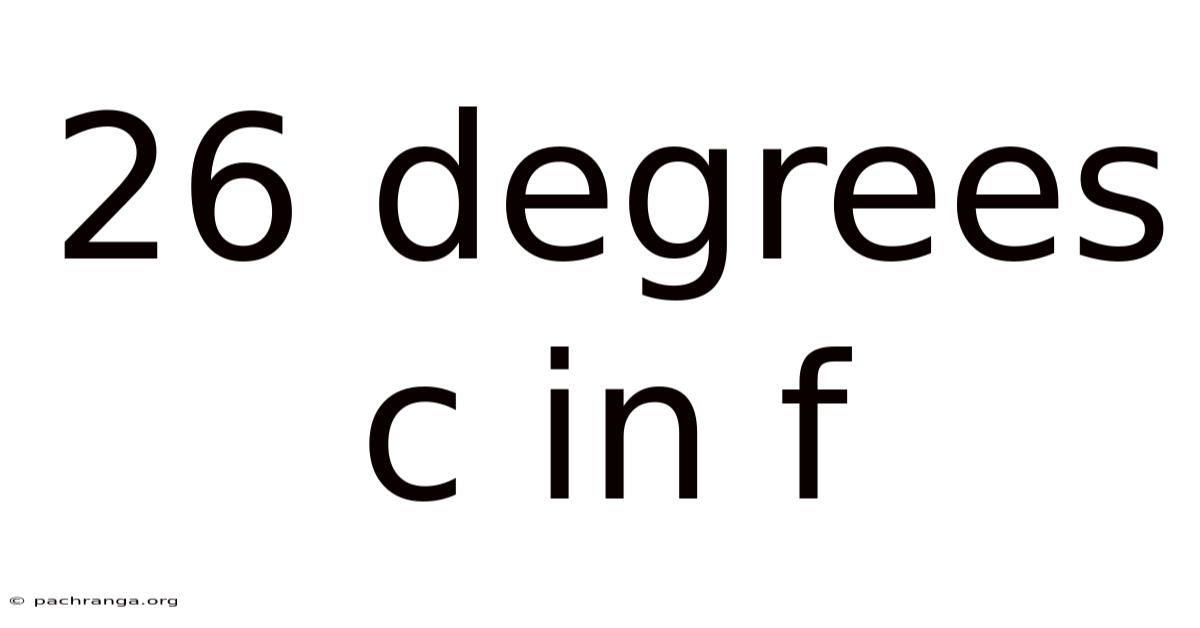
Table of Contents
26 Degrees Celsius in Fahrenheit: A Comprehensive Guide to Temperature Conversion
Are you wondering what 26 degrees Celsius is in Fahrenheit? This seemingly simple question opens the door to a broader understanding of temperature scales, their history, and practical applications in everyday life. This comprehensive guide will not only answer your question about converting 26°C to Fahrenheit but also delve into the intricacies of temperature measurement and conversion, providing you with a wealth of knowledge you can use in various situations.
Understanding Celsius and Fahrenheit
Before we dive into the conversion, let's briefly understand the two temperature scales involved: Celsius (°C) and Fahrenheit (°F).
-
Celsius (°C): Also known as the centigrade scale, Celsius is a metric system scale based on the freezing and boiling points of water. Water freezes at 0°C and boils at 100°C at standard atmospheric pressure. It's widely used globally, especially in scientific contexts and most parts of the world.
-
Fahrenheit (°F): This scale is primarily used in the United States and a few other countries. Its defining points are the freezing point of water at 32°F and the boiling point at 212°F. The scale is less intuitive than Celsius, with its origins rooted in early temperature measurement techniques.
Converting 26 Degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit
The conversion formula from Celsius to Fahrenheit is:
°F = (°C x 9/5) + 32
Let's plug in 26°C:
°F = (26 x 9/5) + 32 = (46.8) + 32 = 78.8°F
Therefore, 26 degrees Celsius is equal to 78.8 degrees Fahrenheit.
The Science Behind Temperature Scales
Temperature is a fundamental concept in physics, representing the average kinetic energy of the particles within a substance. The higher the temperature, the faster the particles move. Different scales emerged historically due to varying approaches to defining temperature.
-
Early Temperature Scales: Before Celsius and Fahrenheit, various scales existed, often based on arbitrary reference points. These early scales lacked standardization, leading to inconsistencies and difficulties in comparing measurements.
-
Anders Celsius and the Centigrade Scale: Anders Celsius, a Swedish astronomer, proposed a scale in 1742 where 0° represented the boiling point of water and 100° the freezing point. This was later inverted to the scale we use today.
-
Gabriel Fahrenheit and His Scale: Gabriel Fahrenheit, a German physicist, developed his scale around 1724. His scale used a mixture of ice, water, and ammonium chloride as a reference point (0°F), and later the freezing point of water (32°F). The boiling point of water became 212°F. While the reasoning behind his specific choices isn't completely clear, it likely reflected his experimental methodology.
-
Kelvin Scale (Absolute Zero): While not directly involved in the 26°C to Fahrenheit conversion, it's essential to mention the Kelvin scale (K). This absolute temperature scale starts at absolute zero (-273.15°C or -459.67°F), the theoretical point where all molecular motion ceases. Scientists often prefer Kelvin due to its absolute nature and its use in various thermodynamic calculations.
Practical Applications of Temperature Conversions
Understanding temperature conversions is crucial in many areas of life:
-
Cooking and Baking: Recipes often specify temperatures in either Celsius or Fahrenheit. Accurate conversion is crucial to ensure successful outcomes.
-
Healthcare: Body temperature measurements are vital in healthcare. Understanding the conversion between Celsius and Fahrenheit ensures accurate interpretation of readings from different thermometers.
-
Weather Forecasting: Weather reports typically provide temperatures in both Celsius and Fahrenheit, depending on the region and audience. Understanding the conversion helps you interpret and compare weather conditions from different sources.
-
Engineering and Manufacturing: Many industrial processes require precise temperature control. Converting between Celsius and Fahrenheit is essential for consistent and accurate operation.
-
Science and Research: While Celsius is predominantly used in scientific settings, understanding conversions is crucial for working with data from different sources or collaborating with colleagues who use Fahrenheit.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Q: Is there an online converter for Celsius to Fahrenheit?
A: Yes, numerous online tools and calculators readily convert Celsius to Fahrenheit and vice versa. These tools provide a quick and convenient way to perform the conversion.
- Q: Why are there two different temperature scales?
A: The existence of Celsius and Fahrenheit stems from historical developments in temperature measurement. Different scientists adopted different reference points and methods leading to two distinct, albeit inter-convertible scales. The persistence of both scales reflects cultural and practical reasons.
- Q: Which scale is more accurate?
A: Both scales are equally accurate in measuring temperature, although Celsius is based on a more logically structured system. The accuracy depends on the precision of the measuring instrument, not the scale used.
- Q: Can I convert from Fahrenheit to Celsius?
A: Absolutely! The reverse conversion formula is: °C = (°F - 32) x 5/9
- Q: What is the significance of 26°C?
A: 26°C is a comfortable temperature for many people, often considered pleasant for indoor environments or outdoor activities in warmer climates. It's a temperature frequently seen during spring or fall in temperate regions.
Beyond the Conversion: Exploring Temperature's Impact
Temperature significantly affects various aspects of our lives and the environment. From the weather patterns that shape our climate to the biological processes that govern life, temperature plays a pivotal role.
-
Climate Change and Global Warming: Understanding temperature changes is crucial for comprehending the impact of climate change and global warming. Accurate temperature monitoring and conversion helps scientists track trends and predict future climate scenarios.
-
Material Science and Engineering: Temperature influences the properties of materials. From melting points to thermal expansion, understanding temperature’s impact is critical for designing and manufacturing products.
-
Biology and Physiology: Biological processes are highly sensitive to temperature variations. Maintaining optimal temperatures is essential for human health, plant growth, and the functioning of ecosystems.
Conclusion
Converting 26 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit (78.8°F) is a simple calculation, yet it opens a world of understanding about temperature measurement, scientific history, and the practical implications of accurate conversions. The ability to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit is not just a mathematical skill, it is a valuable tool with wide-ranging applications in various fields. This guide provides not only a clear understanding of the conversion process but also a broader appreciation for the importance of temperature measurement in our daily lives and the world around us. From cooking a perfect meal to understanding climate change, mastering this seemingly simple conversion is a step towards a more informed and scientifically literate understanding of the world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
195 Cm To Feet Height
Sep 18, 2025
-
Sign Language For Letter A
Sep 18, 2025
-
80 Gradi Fahrenheit In Celsius
Sep 18, 2025
-
72cm Is How Many Inches
Sep 18, 2025
-
98 6 Fahrenheit In Celsius
Sep 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 26 Degrees C In F . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.