3 Degree C To F
pachranga
Sep 15, 2025 · 5 min read
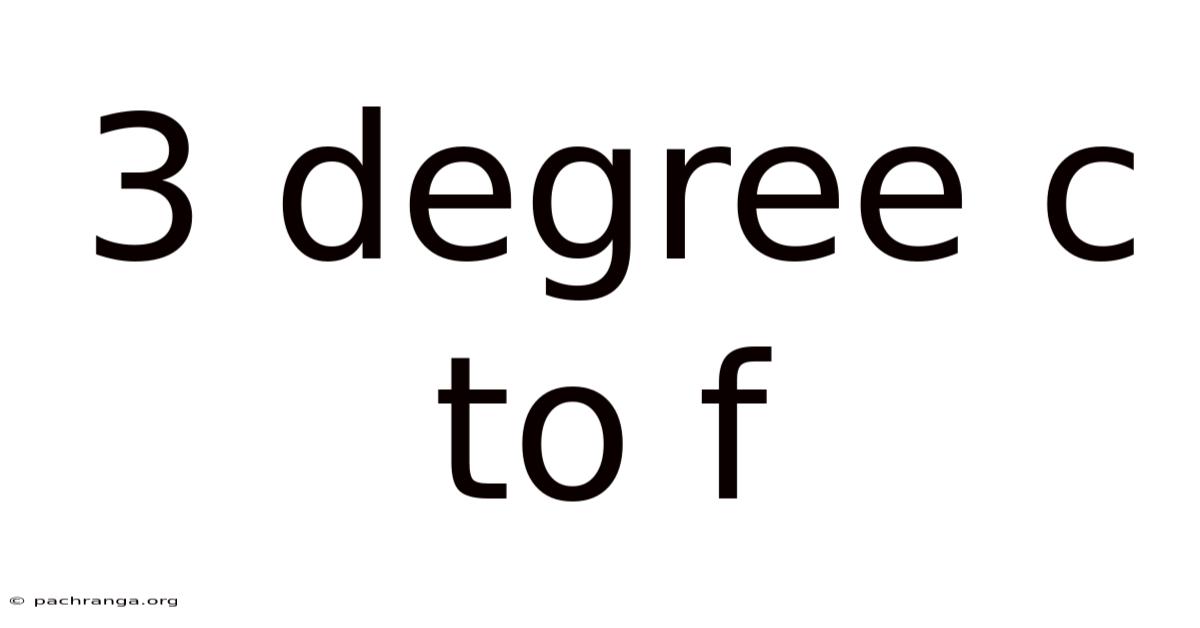
Table of Contents
Converting 3 Degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding temperature conversions is crucial in various fields, from cooking and meteorology to engineering and medicine. This comprehensive guide will delve into the process of converting 3 degrees Celsius (°C) to Fahrenheit (°F), exploring the underlying formula, practical applications, and frequently asked questions. We'll also examine the historical context of these temperature scales and discuss their respective strengths and weaknesses. This will provide a robust understanding of not only the specific conversion but also the broader context of temperature measurement.
Understanding Celsius and Fahrenheit
Before we jump into the conversion, let's briefly review the two scales. The Celsius scale, also known as the centigrade scale, is a metric unit of temperature where 0°C is the freezing point of water and 100°C is its boiling point at sea level. This scale is widely used globally, especially in scientific contexts.
The Fahrenheit scale, on the other hand, is a non-metric unit primarily used in the United States. Water freezes at 32°F and boils at 212°F at sea level. While less common internationally, understanding Fahrenheit remains essential due to its continued use in many parts of the world.
The Conversion Formula: Celsius to Fahrenheit
The fundamental formula for converting Celsius to Fahrenheit is:
°F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
This formula establishes a linear relationship between the two scales, allowing for accurate conversion between them. Let's apply this to our specific case: converting 3°C to °F.
Calculating 3 Degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit
Substituting 3°C into the formula, we get:
°F = (3 × 9/5) + 32
°F = (27/5) + 32
°F = 5.4 + 32
°F = 37.4
Therefore, 3 degrees Celsius is equal to 37.4 degrees Fahrenheit.
Practical Applications of Temperature Conversion
The ability to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit is essential in numerous applications:
- Cooking: Recipes often specify temperatures in either Celsius or Fahrenheit. Accurate conversion ensures the desired cooking results.
- Medicine: Body temperature is frequently measured in both scales. Converting between them is vital for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
- Meteorology: Weather reports often provide temperatures in both scales, accommodating diverse audiences.
- Engineering: Many engineering processes require precise temperature control, making accurate conversion crucial.
- Science: Scientific research frequently utilizes both scales, demanding a thorough understanding of their interconversion.
A Deeper Dive into the History of Temperature Scales
Understanding the historical development of temperature scales provides valuable context for their current usage. Anders Celsius, a Swedish astronomer, developed the Celsius scale in the 1740s. His original scale was inverted, with 0° representing the boiling point of water and 100° the freezing point. This was later reversed to the scale we use today.
Gabriel Fahrenheit, a German physicist, developed the Fahrenheit scale in the early 1700s. His scale was based on a mixture of ice, water, and ammonium chloride, with 0°F representing the freezing point of this mixture. The boiling point of water was later established as 212°F.
Why are there different scales?
The existence of multiple temperature scales, particularly Celsius and Fahrenheit, reflects the historical evolution of scientific measurement. Different scientists, working independently, developed their own scales based on different reference points and methodologies. While the Celsius scale has become the international standard for scientific purposes due to its logical and easily understandable structure based on the properties of water, the Fahrenheit scale persists in some regions due to established usage and cultural inertia.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Celsius and Fahrenheit
Each scale has its own advantages and disadvantages:
Celsius:
- Advantages: Logically based on the freezing and boiling points of water, making it easy to understand and remember. Widely used internationally in scientific and everyday life.
- Disadvantages: Less familiar to some populations (primarily in the US).
Fahrenheit:
- Advantages: Historically established in some regions, leading to continued use in certain applications.
- Disadvantages: Less intuitive and more difficult to understand than Celsius. The scale's arbitrary reference points make it less logical and harder to remember.
Beyond the Conversion: Understanding Temperature and Heat
It's essential to distinguish between temperature and heat. Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance. Heat, on the other hand, is the transfer of energy between objects at different temperatures. While the conversion from Celsius to Fahrenheit deals directly with temperature measurement, understanding the relationship between temperature and heat provides a more comprehensive grasp of thermal phenomena.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Can I use an online converter for this calculation?
A1: Yes, many online converters are available that can quickly perform Celsius to Fahrenheit conversions. However, understanding the underlying formula is crucial for a deeper understanding of the process.
Q2: Is the conversion formula always accurate?
A2: The formula is accurate under standard atmospheric pressure. At significantly different pressures, the boiling and freezing points of water will slightly vary, affecting the precision of the conversion.
Q3: Are there other temperature scales besides Celsius and Fahrenheit?
A3: Yes, several other scales exist, including the Kelvin scale, which is the absolute temperature scale used in many scientific contexts. The Kelvin scale's zero point (0 K) represents absolute zero, the theoretical point at which all molecular motion ceases.
Q4: Why is understanding temperature conversion important?
A4: Understanding temperature conversions is vital for accurate measurement and interpretation of data across various disciplines, ensuring consistent and reliable results in fields ranging from culinary arts to advanced scientific research. Misinterpretations due to incorrect conversions can have significant consequences.
Q5: How do I convert Fahrenheit to Celsius?
A5: The reverse conversion formula is: °C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
Conclusion: Mastering Temperature Conversions
Converting 3 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit, while a seemingly simple task, offers a gateway to a broader understanding of temperature measurement, its historical development, and its diverse applications. By grasping the underlying formula and its practical implications, we can appreciate the importance of accurate conversions in various aspects of life and scientific endeavor. Remember, while online tools can expedite the process, comprehending the methodology behind the conversion remains key to a robust and insightful understanding of temperature scales. This allows for more than just a numerical answer; it fosters a deeper comprehension of the concepts involved and their significance in a multitude of fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
104 Degrees Fahrenheit In Celsius
Sep 15, 2025
-
How Far Is 1500 Km
Sep 15, 2025
-
80 Degrees C In F
Sep 15, 2025
-
How Tall Is 130 Cm
Sep 15, 2025
-
How Many Inches In 50cm
Sep 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 3 Degree C To F . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.