6 Degrees C In F
pachranga
Sep 14, 2025 · 6 min read
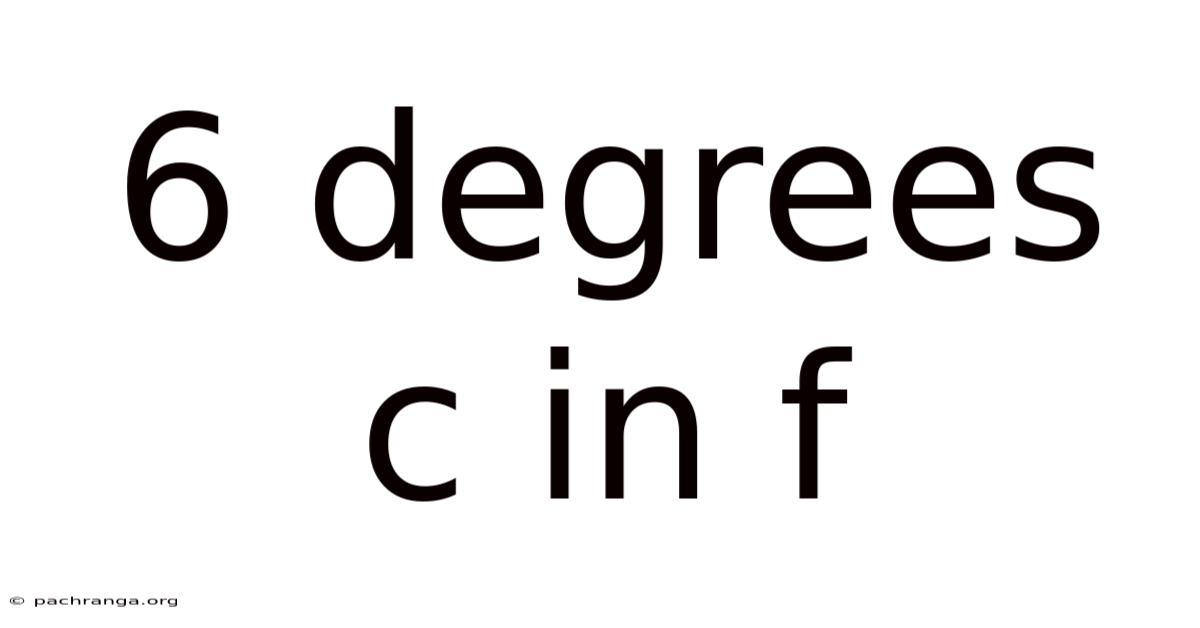
Table of Contents
Decoding 6 Degrees Celsius: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Converting Temperatures
Are you wondering how to convert 6 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit? Understanding temperature conversions is crucial in various fields, from cooking and everyday life to scientific research and meteorology. This comprehensive guide will not only show you how to convert 6°C to °F but also delve deeper into the concepts of temperature scales, their history, and practical applications. We'll explore the science behind temperature measurement and equip you with the knowledge to confidently handle temperature conversions in the future. This article covers the conversion process, explores the significance of 6°C in different contexts, and addresses frequently asked questions.
Understanding Temperature Scales: Celsius and Fahrenheit
Before diving into the conversion, let's understand the two most commonly used temperature scales: Celsius (°C) and Fahrenheit (°F).
-
Celsius (°C): Also known as the centigrade scale, Celsius is a metric unit based on the freezing and boiling points of water. Water freezes at 0°C and boils at 100°C at standard atmospheric pressure. It's widely used globally, particularly in scientific contexts.
-
Fahrenheit (°F): Primarily used in the United States, Fahrenheit has a different reference point. Water freezes at 32°F and boils at 212°F at standard atmospheric pressure. The scale was developed by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in the early 18th century.
Converting 6 Degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit
The formula for converting Celsius to Fahrenheit is:
°F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
Let's apply this to convert 6°C:
°F = (6 × 9/5) + 32 = (54/5) + 32 = 10.8 + 32 = 42.8°F
Therefore, 6 degrees Celsius is equal to 42.8 degrees Fahrenheit.
The Significance of 6°C: A Closer Look
While seemingly an arbitrary temperature, 6°C holds significance in various contexts:
-
Climate and Weather: A temperature of 6°C is considered cool to many, falling within a range often experienced during spring or autumn in temperate climates. It's a temperature where some people might wear a light jacket or sweater outdoors. In agricultural contexts, 6°C can influence plant growth and development; some plants might experience slowed growth or even damage at this temperature.
-
Refrigeration and Food Safety: 6°C is within the danger zone for food safety. While not as critical as temperatures closer to room temperature, keeping food consistently below 4°C (39°F) is crucial to prevent bacterial growth and foodborne illnesses. This temperature is frequently cited in guidelines for safe food storage and handling.
-
Aquatic Environments: In aquatic ecosystems, 6°C can impact the survival and behavior of aquatic organisms. Many fish species have specific temperature preferences, and deviations from these optimal temperatures can lead to stress, reduced reproductive success, or even mortality. Changes in water temperature, even subtle ones like fluctuations from 6°C to a few degrees higher or lower, can trigger significant ecological consequences.
-
Industrial Processes: Certain industrial processes, especially those involving chemical reactions or material properties, are sensitive to temperature variations. Maintaining a precise temperature like 6°C might be necessary for the successful execution of these processes, ensuring quality control and safety. For instance, some chemical reactions have optimal temperatures that need to be meticulously controlled to achieve desired results.
-
Human Physiology: While 6°C is not a comfortable temperature for prolonged human exposure, understanding its implications in the context of hypothermia is crucial. Prolonged exposure to low temperatures like 6°C can lead to hypothermia, a dangerous condition where the body loses heat faster than it can produce it. Understanding how the body reacts to these temperatures is vital for survival in cold environments.
Beyond the Conversion: Exploring Temperature Measurement
Understanding temperature scales goes hand-in-hand with understanding how temperature is actually measured. Various instruments are used for this purpose, including:
-
Thermometers: These are the most common tools for measuring temperature. They come in various forms, from simple liquid-in-glass thermometers to digital thermometers and specialized instruments for scientific applications. The principle behind most thermometers is the expansion and contraction of a substance (liquid or gas) in response to changes in temperature.
-
Thermocouples: These are electrical devices used to measure temperature based on the Seebeck effect, which describes the voltage generated when two dissimilar conductors are joined at different temperatures. They are particularly useful for measuring high temperatures.
-
Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs): RTDs utilize the principle that the electrical resistance of a material changes with temperature. They provide highly accurate temperature measurements and are often used in industrial settings.
-
Infrared Thermometers (Non-Contact Thermometers): These measure temperature by detecting the infrared radiation emitted by an object. They are useful when direct contact with the object is not feasible.
The History of Temperature Scales: A Brief Overview
The development of temperature scales has been a fascinating journey, with several scientists contributing to their refinement:
-
Gabriel Daniel Fahrenheit (1714): Fahrenheit established a scale using a mixture of ice, water, and ammonium chloride as his zero point, and the freezing point of water as 32 degrees. This scale remains prevalent in some parts of the world today.
-
Anders Celsius (1742): Celsius introduced the centigrade scale, now known as the Celsius scale, which defined the freezing point of water as 0 degrees and the boiling point as 100 degrees. This scale is based on the metric system and is widely used in scientific applications globally.
-
Lord Kelvin (1848): Lord Kelvin proposed the absolute temperature scale, now known as the Kelvin scale. This scale starts at absolute zero, the theoretical point where all molecular motion ceases. Kelvin is an important scale in thermodynamics and scientific research.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Q: Why are there different temperature scales?
A: Different temperature scales were developed independently and based on different reference points. The choice of scale often depends on historical context, geographical location, and specific applications.
- Q: Which temperature scale is more accurate?
A: All temperature scales are equally accurate in their respective ranges. The choice of scale depends on the context and the desired precision. The Kelvin scale is preferred in scientific applications as it uses an absolute zero point.
- Q: Can I use an online converter for Celsius to Fahrenheit?
A: Yes, many online converters are available to quickly convert Celsius to Fahrenheit and vice versa. However, understanding the underlying formula is crucial for broader understanding and application.
- Q: What is the significance of absolute zero?
A: Absolute zero (0 Kelvin or -273.15°C) is the theoretical point at which all molecular motion ceases. It represents the lowest possible temperature and is a fundamental concept in thermodynamics.
- Q: How does temperature affect chemical reactions?
A: Temperature significantly influences the rate of chemical reactions. Generally, increasing temperature increases the reaction rate, as molecules move faster and collide more frequently. However, very high temperatures can also break down molecules, affecting the reaction.
Conclusion: Mastering Temperature Conversions and Beyond
Converting 6°C to 42.8°F is just the starting point. Understanding the nuances of temperature scales, their history, and practical applications broadens our knowledge of the physical world. Whether you're a student, a chef, a scientist, or simply curious about the world around you, appreciating the interconnectedness of temperature measurements, conversion techniques, and their implications across various disciplines opens doors to deeper learning and a more informed understanding of the environment and the universe itself. From understanding weather patterns to ensuring food safety, mastering temperature conversions is a valuable skill that extends far beyond simple calculations.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
175 Cm To Feet Inches
Sep 14, 2025
-
Convert 55 Fahrenheit To Celsius
Sep 14, 2025
-
300 C Is What Fahrenheit
Sep 14, 2025
-
28 Deg C To F
Sep 14, 2025
-
32 Degree Celcius To Farenheit
Sep 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 6 Degrees C In F . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.