86 Deg F To C
pachranga
Sep 04, 2025 · 6 min read
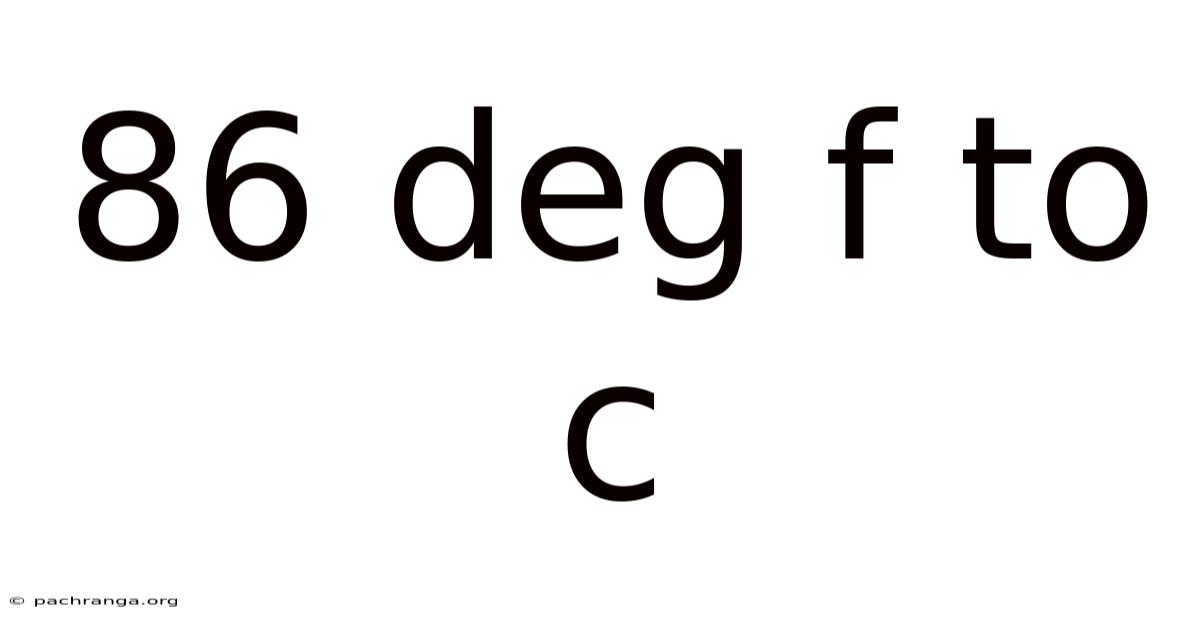
Table of Contents
Converting 86 Degrees Fahrenheit to Celsius: A Comprehensive Guide
Have you ever wondered how to convert temperatures from Fahrenheit to Celsius? Understanding temperature conversions is crucial in various fields, from cooking and baking to scientific research and everyday life. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of converting 86 degrees Fahrenheit (°F) to Celsius (°C), explaining the underlying formula, providing step-by-step instructions, and exploring the practical applications of this conversion. We'll also delve into the history of both temperature scales and answer some frequently asked questions.
Understanding Fahrenheit and Celsius
Before we jump into the conversion, let's briefly understand the two scales. The Fahrenheit scale (°F), developed by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in the early 18th century, is a temperature scale where the freezing point of water is 32°F and the boiling point is 212°F at standard atmospheric pressure. Conversely, the Celsius scale (°C), also known as the centigrade scale, was developed by Anders Celsius and has 0°C as the freezing point of water and 100°C as the boiling point, again at standard atmospheric pressure. The key difference lies in the size of the degree intervals and the starting points.
The Conversion Formula: From Fahrenheit to Celsius
The formula for converting Fahrenheit to Celsius is:
°C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
This formula takes the Fahrenheit temperature, subtracts 32 (to adjust for the difference in freezing points), and then multiplies the result by 5/9 (to account for the different size of the degree intervals).
Step-by-Step Conversion of 86°F to °C
Let's apply the formula to convert 86°F to °C:
-
Subtract 32: 86°F - 32°F = 54°F
-
Multiply by 5/9: 54°F × (5/9) = 30°C
Therefore, 86°F is equal to 30°C.
Practical Applications of Temperature Conversions
The ability to convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius is vital in numerous situations:
-
Cooking and Baking: Recipes from different countries might use different temperature scales. Converting ensures accurate baking and cooking results. Knowing that 86°F (30°C) is a warm temperature helps in tasks like proofing yeast or making certain types of dough.
-
Scientific Research: Many scientific experiments and observations require precise temperature control and recording. Converting between Fahrenheit and Celsius ensures consistent data reporting and allows for comparisons across studies using different scales. A consistent temperature is often crucial for various chemical and biological processes.
-
Medicine and Healthcare: Body temperature readings are sometimes given in Fahrenheit, but healthcare professionals often work with Celsius for record-keeping and medical calculations. Accurate conversions are essential for diagnosis and treatment. Understanding that 86°F (30°C) is slightly above average human body temperature is important in evaluating a patient's health.
-
Meteorology and Climate Science: Weather reports and climate data are often reported in both Fahrenheit and Celsius, making conversions necessary for understanding and comparing weather patterns across different regions and time periods.
-
Engineering and Manufacturing: Many industrial processes require precise temperature control. Converting between scales is crucial for ensuring equipment operates within the correct parameters and products are manufactured according to specifications. Certain materials may behave differently at various temperatures, hence accurate conversion is needed.
-
Everyday Life: Understanding temperature conversions can help you adjust to different climates and make informed decisions related to clothing, activities, and personal comfort.
A Deeper Dive into the History of Temperature Scales
The Fahrenheit scale, invented by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit, was initially based on three reference points: the temperature of a mixture of ice, water, and ammonium chloride (0°F), the temperature of water and ice (32°F), and the temperature of the human body (approximately 96°F). Although the scale is still used in some countries, particularly the United States, it has been largely superseded by the Celsius scale in scientific and international contexts.
The Celsius scale, also known as the centigrade scale, was developed by Anders Celsius in the 18th century. The scale was originally defined with 0°C as the boiling point of water and 100°C as the freezing point. This was later reversed, creating the scale we use today. The Celsius scale's simplicity and logical structure have made it the preferred scale in scientific applications and internationally. It's part of the International System of Units (SI).
Beyond the Basic Conversion: Considering Significant Figures and Precision
While the conversion of 86°F to 30°C is straightforward, it's important to consider significant figures and the level of precision required depending on the context. The number 86°F implies two significant figures. Rounding the result to 30°C also reflects this precision. However, in applications needing higher accuracy, a more precise calculation and reporting might be necessary. For example, using a calculator, the result of (86-32) * 5/9 is actually 29.999... which rounds up to 30, but that extra precision could be relevant in certain fields.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions about Temperature Conversions
Q: Why is the conversion formula (°F - 32) × 5/9 and not a simpler method?
A: The formula reflects the difference in the zero points and the size of the degree intervals between Fahrenheit and Celsius. Subtracting 32 adjusts for the difference in the freezing points of water (32°F vs 0°C), and multiplying by 5/9 accounts for the fact that a Celsius degree is larger than a Fahrenheit degree.
Q: Can I convert from Celsius to Fahrenheit?
A: Absolutely! The reverse conversion formula is: °F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
Q: Are there other temperature scales besides Fahrenheit and Celsius?
A: Yes! The Kelvin scale (K) is an absolute temperature scale where 0 K represents absolute zero, the theoretical point at which all molecular motion ceases. It's widely used in scientific applications. Other historical scales exist but are less frequently used today.
Q: Why is it important to understand temperature conversions?
A: Understanding temperature conversions is crucial for clear communication, accurate measurements, and ensuring safety and efficacy across various fields. It ensures consistency and avoids errors in scientific research, cooking, healthcare, and numerous other aspects of life.
Conclusion: Mastering Fahrenheit to Celsius Conversions
Converting 86°F to 30°C is a simple yet essential skill. Understanding the underlying formula, its application in various contexts, and the historical background of these temperature scales provides a solid foundation for anyone working with temperature measurements. This knowledge enhances accuracy, promotes effective communication, and contributes to a deeper understanding of the physical world around us. Remember, the ability to seamlessly convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius is a valuable tool that transcends academic study and finds practical application in everyday life.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Convert 61 Inches To Feet
Sep 04, 2025
-
156cm In Feet And Inches
Sep 04, 2025
-
260 Km Hr To Mph
Sep 04, 2025
-
Convert 21 C To F
Sep 04, 2025
-
How Long Is 33 Cm
Sep 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 86 Deg F To C . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.